MUSEOLOGY AND CONSERVATION
PAPER – II
Note : This paper contains hundred (100) objective type questions of two (2) marks each. All questions are compulsory.
1. Which of the following is a dynamic technique of Interpretation ?
(1) Tableaux
(2) Models
(3) Drama
(4) Guide books
2. ‘Reconstruction of a Tribal house’ is :
(1) Thematic exhibition
(2) Ecological exhibition
(3) Systematic exhibition
(4) Historical exhibition
3. Thymol is used in museums as :
(1) Insecticide
(2) Fungicide
(3) Rodenticide
(4) Weedicide
4. AAM stands for :
(1) American Alliance of Museums
(2) American Association of Museums
(3) Association of American Museums
(4) Alliance of American Museums
5. Which of the following is ICOM’s international committee for collecting ?
(1) CIDOC
(2) COMCOL
(3) CAMOC
(4) UMAC
6. HEPA filters are used to :
(1) Filter particulate matter
(2) Filter UV rays
(3) Filter IR rays
(4) Filter Ozone
7. The most important factor to consider before applying a facing on a painting is that :
(1) It can be successfully removed.
(2) It cannot be removed.
(3) It is hygroscopic.
(4) It is transparent.
8. British Museum Leather Dressing mixture does not contain :
(1) Paraffin wax
(2) Anhydrous lanolin
(3) Hexane
(4) Bees wax
9. Benzotriazole is used for treating :
(1) Iron objects
(2) Bronze objects
(3) Silver objects
(4) Leaded objects
10. The safest way of dealing with potentially unstable ‘weeping glass’ objects is to ensure that they are kept under :
(1) Humid conditions
(2) Dry conditions
(3) Low temperature
(4) Ultraviolet rays
11. The Scientific method of dating based on the analysis of patterns of tree rings, also known as growth rings is called :
(1) Thermoluminescence dating
(2) Radiocarbon dating
(3) Dendrochronology
(4) Stratigraphy
12. A UV monitor is used to measure :
(1) the UV component of light
(2) the intensity of UV radiation
(3) the exposure to UV radiation
(4) level of illumination
13. Light damage is cumulative. It means that :
(1) Lower levels of illumination will mean less damage over the long term.
(2) Lower levels of illumination will mean more damage over the long term.
(3) Lower levels of illumination will mean more damage over the short term.
(4) Higher levels of illumination will mean less damage over the long term.
14. What is the exposure, in megalux hours, of an oil painting displayed for 48 weeks in a museum which is open for eight hours a day, seven days a week and where light falling on the painting has been measured as 150 lux ?
(1) 0.4032
(2) 4.032
(3) 4032
(4) 4032000
15. Who said “a museum performs its complete office as it is at once gardant, monstrant, and docent” ?
(1) John Cotton Dana
(2) Benjamin Ives Gilman
(3) George Brown Goode
(4) Dillon Ripley
16. Cloze Test is used to assess :
(1) Legibility of the text
(2) Comprehensibility of the text
(3) Typography of the text
(4) Readability of the text
17. Which one of the followings is used to measure colour changes in paintings and textile due to exposure to light ?
(1) UV lamp
(2) Psychrometer
(3) Stereoscopic binocular microscope
(4) Blue Wool Scale
18. Exit gradient effect means :
(1) visitors follow the straightest line between the entrance and a visible open door.
(2) an open door is an invitation to leave the gallery.
(3) visitors walk into the exhibit environment.
(4) visitors may touch and manipulate objects before leaving the gallery.
19. Victoria Memorial Hall, West Bengal is :
(1) an autonomous body of Ministry of Culture, Govt. of India.
(2) a subordinate office of the Ministry of Culture, Government of India.
(3) an autonomous body of Ministry Culture, Government of West Bengal.
(4) a subordinate office of Ministry Culture, Government of West Bengal.
20. What does ‘a’ stand for in the accession number 85.257.7a ?
(1) quality or grade of the 7th accession
(2) quality or grade of the 7th object of the 257th accession
(3) quality or grade of the first part of the 7th object of the 257th accession
(4) first part of the 7th object of 257th accession
21. Paintings on translucent gauge combined with moving lights to create the impression of movement and scene were the original form of :
(1) Cyclorama
(2) Diorama
(3) Panorama
(4) Tableau
22. Which of the following is effective on all stages of insect pests ?
(1) Ethylene oxide
(2) Paradichlorobenzene
(3) Naphthalene
(4) Thymol
23. Who developed the theory of multiple intelligences ?
(1) John Dewey
(2) Robert Gagne
(3) Carl Rogers
(4) Howard Gardner
24. Silica gel :
(a) can be used as a desiccant.
(b) can be used as a buffering agent.
(c) is non-toxic.
(d) is non-corrosive.
Code :
(1) (a), (b), (c)
(2) (b), (c), (d)
(3) (a), (c), (d)
(4) (a), (b), (c), (d)
25. Colour can be used in exhibitions to :
(a) attract attention
(b) give emphasis
(c) create mood
(d) guide viewing
Code :
(1) (a), (b), (c)
(2) (b), (c), (d)
(3) (b), (c)
(4) (a), (b), (c), (d)
26. A museum can augment its collections by acquiring objects on permanent basis by :
(a) Gifts
(b) Purchases
(c) Fieldwork
(d) Loans
Code :
(1) (a), (b), (c)
(2) (b), (c), (d)
(3) (a), (c), (d)
(4) (a), (b), (c), (d)
27. Excessive humidity can cause :
(a) Weakening of adhesive
(b) Rotting of size
(c) Staining of paper
(d) Blurring of inks
Code :
(1) (a), (b), (c)
(2) (b), (c), (d)
(3) (b), (c)
(4) (a), (b), (c), (d)
28. Which of the following are inherent causes of deterioration in paper ?
(a) High RH
(b) Bleaching residues
(c) Lignin
(d) Unstable sizing
Code :
(1) (a), (b), (c)
(2) (b), (c), (d)
(3) (b), (d)
(4) (a), (b), (c), (d)
29. A plan-budget does not include expenses on :
(a) Salaries
(b) Services such as electricity, water and gas
(c) Superannuation payments
(d) Building maintenance
Code :
(1) (a), (d)
(2) (a), (b), (c)
(3) (b), (c), (d)
(4) (a), (b), (c), (d)
30. Which of the following causes the post-mortem decay of Animals and plant ?
(a) Release of hydrolytic enzymes with in the cell
(b) Interaction of body with pollutants
(c) Attack by Scavengery
(d) Invasion of the Bacteria present in the specimen
Code :
(1) (a), (d)
(2) (a), (b), (c)
(3) (a), (b), (c), (d)
(4) (a), (c), (d)
31. Interpretation :
(a) allows for variation in technique
(b) is systematic instruction
(c) is personal
(d) is impersonal
Code :
(1) (a), (b)
(2) (b), (d)
(3) (a), (c)
(4) (a), (b), (c)
32. Which of the following statements are true ?
(a) Education and Interpretation are the same thing.
(b) A storyteller is a kind of interpreter.
(c) Docents do not need training.
(d) Museum tours can be enhanced by demonstration.
Code :
(1) (a), (b), (c)
(2) (b), (d)
(3) (b), (c), (d)
(4) (a), (c), (d)
33. Which of the following statements are true ?
(a) A museum must accept all gifts.
(b) A collection policy is not required if a museum already has a collection.
(c) A collection is only as important as its documentation.
(d) Collecting was historically the first museum function.
Code :
(1) (a), (c), (d)
(2) (c), (d)
(3) (a), (b), (c)
(4) (a), (b)
34. The Accession Number :
(a) establishes the identity of an object.
(b) ensures safety of an object.
(c) proves that the object belongs to the museum’s collection.
(d) serves as the access key for all documentation concerning an object.
Code :
(1) (a), (c), (d)
(2) (b), (c), (d)
(3) (c), (d)
(4) (a), (b), (c), (d)
35. Which of the following are conductive to mould growth ?
(a) Temperature above 25°C
(b) RH above 65%
(c) Air circulation
(d) Lack of air circulation
Code :
(1) (a), (b), (d)
(2) (b), (c), (d)
(3) (a), (c), (d)
(4) (a), (b), (c), (d)
36. In case of a fire :
(a) Remain Calm
(b) Contact the Fire Department
(c) Inform the press
(d) Do not break windows
Code :
(1) (a), (b), (c)
(2) (b), (c), (d)
(3) (a), (b), (c), (d)
(4) (a), (b), (d)
37. The pure wheat starch paste contains :
(a) Gluten
(b) Amylose
(c) Amylopectin
(d) Cellulose acetate
Code :
(1) (a), (b)
(2) (a), (b), (c)
(3) (b), (c)
(4) (a), (b), (c), (d)
38. Which of the following are examples of Remedial Conservation ?
(a) Disinfestation of textiles
(b) Deacidification of paper
(c) Removal of stains
(d) Storage of prints in solander boxes
Code :
(1) (a), (b)
(2) (a), (b), (c)
(3) (b), (c), (d)
(4) (a), (b), (c), (d)
39. Which of the following statements about organic materials are correct ?
(a) They are animal or vegetable in origin.
(b) They are carbon based with a cellular structure.
(c) They are susceptible to deterioration by light.
(d) They include natural stones, ceramics and glass.
Code :
(1) (a), (b), (c)
(2) (b), (c), (d)
(3) (c), (d)
(4) (a), (b), (c), (d)
40. Guided discovery is :
(a) teacher-led learning method.
(b) learner-led learning method.
(c) characterized by divergent thinking.
(d) characterized by convergent thinking.
Code :
(1) (a), (d)
(2) (a), (b), (c)
(3) (a), (c), (d)
(4) (b), (c), (d)
41. Which of the following would benefit people with mobility difficulties ?
(a) amplification devices
(b) adequate seating in all galleries
(c) wheel chairs
(d) lifts
Code :
(1) (b), (d)
(2) (a), (b), (c)
(3) (b), (c), (d)
(4) (b), (c)
42. Which of the following can be used for communication with/by people with deafness or hearing impairment ?
(a) Sign Language
(b) Lip reading
(c) Braille
(d) Paper and pencil
Code :
(1) (a), (d)
(2) (a), (c), (d)
(3) (a), (b), (c), (d)
(4) (a), (b), (d)
43. Which of the following are scholarly publications ?
(a) Journal
(b) Catalogue
(c) Monograph
(d) Pamphlet
Code :
(1) (a), (b), (c), (d)
(2) (a), (b), (c)
(3) (a), (c), (d)
(4) (a), (d)
44. Which of the following should influence the decision of a museum to acquire an object ?
(a) Significance of the object
(b) Availability of resources
(c) Liking of the curator
(d) Scope of the museum’s collection
Code :
(1) (a), (b), (d)
(2) (a), (c), (b)
(3) (a), (d)
(4) (a), (b), (c), (d)
45. Assertion (A) : Wood can warp upon drying or moistening.
Reason (R) : Because of the unequal loss or gain of moisture in longitudinal, radial and tangential sides of the wood.
Code :
(1) (A) is wrong, but (R) is right.
(2) (A) is right, but (R) is wrong.
(3) Both (A) and (R) are right.
(4) Both (A) and (R) are wrong.
46. Assertion (A) : Where museum activities involve a contemporary community or its heritage, acquisitions should only be made based on informed and mutual consent.
Reason (R) : So that exploitation of the owner or informants is avoided and the wishes of the community involved are respected.
Code :
(1) (A) is wrong, but (R) is right.
(2) (A) is right, but (R) is wrong.
(3) Both (A) and (R) are right.
(4) Both (A) and (R) are wrong.
47. Assertion (A) : Conservators can bring back faded colours of painting.
Reason (R) : Effect of light is reversable.
Code :
(1) (A) is wrong, but (R) is right.
(2) (A) is right, but (R) is wrong.
(3) Both (A) and (R) are right.
(4) Both (A) and (R) are wrong.
48. Assertion (A) : While packing an object with bubble pack, the bubble side should face away from the object’s surface.
Reason (R) : Bubbles can leave impressions on the objects surface.
Code :
(1) (A) is wrong, but (R) is right.
(2) (A) is right, but (R) is wrong.
(3) Both (A) and (R) are right.
(4) Both (A) and (R) are wrong.
49. Assertion (A) : While restoring a glass artifact, restorers use an adhesive that has a refractive index similar to the glass.
Reason (R) : So that the adhesive does not react with the glass.
Code :
(1) (A) is wrong, but (R) is right.
(2) (A) is right, but (R) is wrong.
(3) Both (A) and (R) are right.
(4) Both (A) and (R) are wrong.
50. Assertion (A) : Restorations should be invisible or unnoticeable to the viewers.
Reason (R) : Conservators want viewers to believe that the object is undamaged.
Code :
(1) (A) is wrong, but (R) is right.
(2) (A) is right, but (R) is wrong.
(3) Both (A) and (R) are right.
(4) Both (A) and (R) are wrong.
51. Assertion (A) : To measure light level, the light meter should face the object.
Reason (R) : To get an accurate reading of light reflected by the object.
Code :
(1) (A) is wrong, but (R) is right.
(2) (A) is right, but (R) is wrong.
(3) Both (A) and (R) are right.
(4) Both (A) and (R) are wrong.
52. Assertion (A) : Use of acrylic sheet is preferred over varnish to filter UV rays.
Reason (R) : Acrylic sheet is more convenient lasts longer, and does the job better.
Code :
(1) (A) is wrong, but (R) is right.
(2) (A) is right, but (R) is wrong.
(3) Both (A) and (R) are right.
(4) Both (A) and (R) are wrong.
53. Assertion (A) : Paper items should never be in a partial shadow cast by another item, show case edge, polyester strap, suspension chain, etc.
Reason (R) : Because this will cause differential fading.
Code :
(1) (A) is wrong, but (R) is right.
(2) (A) is right, but (R) is wrong.
(3) Both (A) and (R) are right.
(4) Both (A) and (R) are wrong.
54. Assertion (A) : Museum Ethics need to be followed strictly by museum workers.
Reason (R) : Because their violation leads to Punishment.
Code :
(1) (A) is wrong, but (R) is right.
(2) (A) is right, but (R) is wrong.
(3) Both (A) and (R) are right.
(4) Both (A) and (R) are wrong.
55. Assertion (A) : A water logged wooden object will retain its shape as long as it is kept wet.
Reason (R) : If the water evaporates or is removed, the resulting surface tension forces of the evaporating water cause the weakened cell walls to collapse.
Code :
(1) (A) is wrong, but (R) is right.
(2) (A) is right, but (R) is wrong.
(3) Both (A) and (R) are right.
(4) Both (A) and (R) are wrong.
56. Assertion (A) : Polished silver objects should not be handled with bare hands.
Reason (R) : Salts and Oils from skin can etch into the polished silver objects and may cause permanent damage.
Code :
(1) (A) is wrong, but (R) is right.
(2) (A) is right, but (R) is wrong.
(3) Both (A) and (R) are right.
(4) Both (A) and (R) are wrong.
57. Assertion (A) : Gum Arabic is problematic as a consolidant for conservation purposes.
Reason (R) : Because of its tendency to become brittle upon aging.
Code :
(1) (A) is wrong, but (R) is right.
(2) (A) is right, but (R) is wrong.
(3) Both (A) and (R) are right.
(4) Both (A) and (R) are wrong.
58. Assertion (A) : In temperate climates, electric fans can improve the environment of collection holding spaces.
Reason (R) : By circulating the air and thereby creating micro-climates that may prevent growth of micro-organisms.
Code :
(1) (A) is wrong, but (R) is right.
(2) (A) is right, but (R) is wrong.
(3) Both (A) and (R) are right.
(4) Both (A) and (R) are wrong.
59. Assertion (A) : Before using gelatin as consolidant consider the future storage and display of object to be treated.
Reason (R) : Because it is hygroscopic and can support mould growth in conditions of high relative humidity. It becomes brittle under excessively dry conditions.
Code :
(1) (A) is wrong, but (R) is right.
(2) (A) is right, but (R) is wrong.
(3) Both (A) and (R) are right.
(4) Both (A) and (R) are wrong.
60. Assertion (A) : When developing exhibit spaces, gradually decrease lighting from the entrance.
Reason (R) : The eye requires time to adjust when moving from a bright area to a dimly lighted space.
Code :
(1) (A) is wrong, but (R) is right.
(2) (A) is right, but (R) is wrong.
(3) Both (A) and (R) are right.
(4) Both (A) and (R) are wrong.
61. Assertion (A) : An object brought to a museum for donation should be immediately given a code and entered in the Accession Register.
Reason (R) : The information contained in the Accession Register will help in deciding whether the object is suitable for acceptance or not.
Code :
(1) (A) is wrong, but (R) is right.
(2) (A) is right, but (R) is wrong.
(3) Both (A) and (R) are right.
(4) Both (A) and (R) are wrong.
62. Assertion (A) : Each whole pH value below 7 is ten times more acidic then the next higher value.
Reason (R) : The pH scale is Logarithmic.
Code :
(1) (A) is wrong, but (R) is right.
(2) (A) is right, but (R) is wrong.
(3) Both (A) and (R) are right.
(4) Both (A) and (R) are wrong.
63. Assertion (A) : Avoid using rubber-based materials for storage or packing of ivory objects.
Reason (R) : As these can produce unnatural yellowing of ivory.
Code :
(1) (A) is wrong, but (R) is right.
(2) (A) is right, but (R) is wrong.
(3) Both (A) and (R) are right.
(4) Both (A) and (R) are wrong.
64. Assertion (A) : Plastics are subject to degradation by light, heat, moisture and pollutants.
Reason (R) : Because they are organic.
Code :
(1) (A) is wrong, but (R) is right.
(2) (A) is right, but (R) is wrong.
(3) Both (A) and (R) are right.
(4) Both (A) and (R) are wrong.
65. Arrange the following stages of New Exhibition development in order :
(a) Concept development and Testing.
(b) Idea generation and screening.
(c) Summative Evaluation.
(d) Exhibition development.
Code :
(1) (a), (d), (b), (c)
(2) (b), (a), (d), (c)
(3) (a), (b), (c), (d)
(4) (b), (c), (d), (a)
66. Arrange the following stages of preparation of Insect specimen for Resin embedding.
(a) Preventive Coating
(b) Positioning
(c) dehydration
(d) Narcotization
Code :
(1) (a), (c), (d), (b)
(2) (b), (d), (c), (a)
(3) (d), (b), (c), (a)
(4) (d), (c), (b), (a)
67. Arrange the following stages of planning an advertising campaign in order.
(a) Deciding the proper theme
(b) Scheduling of the Media
(c) Know the Target Audience
(d) Selection of Media
Code :
(1) (c), (a), (d), (b)
(2) (d), (b), (c), (a)
(3) (a), (d), (b), (c)
(4) (b), (c), (d), (a)
68. Arrange the following cognitive levels in order of Bloom’s Taxonomy.
(a) Comprehension
(b) Knowledge
(c) Evaluation
(d) Analysis
Code :
(1) (b), (d), (c), (a)
(2) (b), (a), (d), (c)
(3) (d), (b), (a), (c)
(4) (c), (a), (b), (d)
69. Arrange the following departments of Museology in order of their establishment :
(a) Dept. of Museology, University of Calcutta.
(b) Dept. of Museology Aligarh Muslim, University.
(c) Dept. of Museology, National Museum Institute.
(d) Dept. of Museology, The M.S. University of Baroda.
Code :
(1) (b), (d), (a), (c)
(2) (c), (a), (d), (b)
(3) (d), (a), (b), (c)
(4) (d), (a), (c), (b)
70. Arrange the following museums in order of their establishment.
(a) Regional Museum of Natural History, Bhubneshwar.
(b) Regional Museum of Natural History, Swai Madhopur
(c) Regional Museum of Natural History, Bhopal
(d) Regional Museum of Natural History, Mysore
Code :
(1) (b), (d), (a), (c)
(2) (c), (a), (d), (b)
(3) (d), (a), (c), (b)
(4) (d), (c), (a), (b)
71. Arrange the following stages of organising visit of school children to a museum in order.
(a) Class preparation
(b) Story telling session
(c) Writing a letter of thanks to the museum
(d) Teacher’s preparatory visit to museum
Code :
(1) (d), (b), (a), (c)
(2) (c), (b), (a), (d)
(3) (d), (a), (b), (c)
(4) (a), (b), (c), (d)
72. Arrange the following stages of Documentation Procedures, after an object arrives at the museum, in order.
(a) Decision taken to accept the object
(b) Complete entry Register
(c) Enter details in the Accession Register
(d) Allocate and Mark Accession Number
Code :
(1) (b), (a), (d), (c)
(2) (b), (d), (c), (a)
(3) (c), (b), (d), (a)
(4) (a), (b), (c), (d)
73. Arrange the various stages in order of their occurance in observing Weeping Glass phenomenon.
(a) Accumulation of water droplets on the surface of glass
(b) Combination of Hydroxyl ions with sodium and potassium
(c) Formation of deliquiscent salts
(d) Rise in Relative Humidity above 42%
Code :
(1) (b), (a), (d), (c)
(2) (d), (b), (c), (a)
(3) (d), (c), (b), (a)
(4) (a), (c), (d), (b)
74. Arrange the following steps in the conservation of a metal object in order of their occurance.
(a) Removal of corrosion products
(b) Application of protective layer
(c) Identification of metal
(d) Examination and documentation of conservation status
Code :
(1) (d), (b), (c), (a)
(2) (d), (a), (b), (c)
(3) (d), (c), (a), (b)
(4) (c), (d), (b), (a)
75. Arrange the following metals in order of their increasing passivity.
(a) Gold
(b) Iron
(c) Zinc
(d) Lead
Code :
(1) (c), (b), (d), (a)
(2) (c), (d), (b), (a)
(3) (a), (c), (b), (d)
(4) (c), (b), (a), (d)
76. Arrange the following periods in Chronological order.
(a) Iron age
(b) Bronze age
(c) Copper age
(d) Stone age
Code :
(1) (a), (b), (c), (d)
(2) (d), (c), (b), (a)
(3) (d), (b), (a), (c)
(4) (b), (a), (d), (c)
77. Arrange the following events in the history of the National Museum, New Delhi Chronological order.
(a) Inaugration of present building by Dr. Sarvapalli Radhakrishnan
(b) Appointment of Maurice Gwyer Committee
(c) Inaugration by Shri. R.C. Rajagopalachari
(d) Separate institution placed under its own direct control
Code :
(1) (b), (c), (d), (a)
(2) (b), (d), (c), (a)
(3) (b), (a), (d), (c)
(4) (a), (d), (b), (c)
78. Arrange the following parts of anatomy of an oil painting from lowest to highest.
(a) Varnish
(b) Ground
(c) Size
(d) Support
Code :
(1) (d), (a), (b), (c)
(2) (b), (c), (a), (d)
(3) (d), (b), (c), (a)
(4) (d), (c), (b), (a)
79. Match the organisations in List – I with their status in List – II.


80. Match the terms in List – I with their meanings in List – II.


81. Match the items in List – I with the items in List – II.
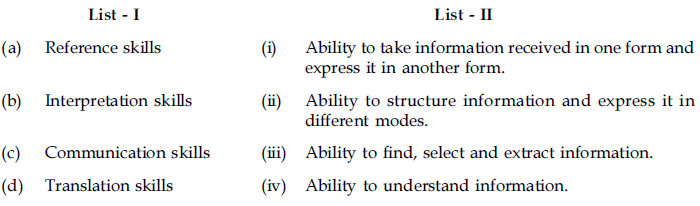

82. Match the types of communication media in List – I with their meanings in List – II.


83. Match the books in List – I with their authors in List – II.


84. Match the research terms in List – I with their meanings in List – II.


85. Match the types of alarm systems in List – I with their functioning in List – II.


86. Match the artists in List – I with their famous works in List – II.

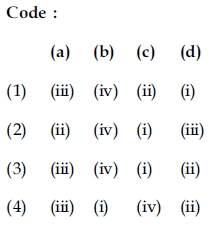
87. Match the items in List – I with items in List – II.


88. Match the objects in List – I with the Museums they are housed in List – II.
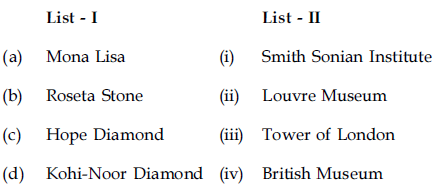

89. Match the statements in List – I with the Periods in List – II.


90. Match the personalities in List – I with their contribution in List – II.


91. Match the conservation terms in List – I with their meanings in List – II.


92. Match the insurance terms in List – I with their meanings in List – II.


93. Match the marketing terms in List – I with their meanings in List – II.


94. Match the terms in List – I with their examples in List – II.


95. Match the Art terms in List – I with their Meanings in List – II.


96. Match the disciplines in List – I with the collections they are concerned with in List – II.


Read the passage below and answer the questions that follow based on your understanding of the same.
Museums have long been considered special places where the authoritative insights of trained experts are shared with members of the public. It is true that we as an institution have something unique to offer the public – the collections we amass and our intellectual insights into the creativity of artists. However, to paraphrase Picasso (and many other artists for that matter), in producing an art work, the artist carries the creative process half way – it is the responsibility of the viewer to
complete the process. This visitor-centred half of the creative process is based on the personalising of symbolic objects. This process is not prescriptive, so institutions cannot control how the personalising occurs. Museums can, however, be supportive of visitors as they personalise their experiences with the art works.
What does the visitor side of creativity look like ? This creativity is idiosyncratic – sometimes tentative, sometimes dogmatic; at times it is intensely moving, other times shocking, while at other times it is insightful. To this writer, visitor-based creativity provides a powerful complement to the intellectual insights of the museum experts. Accordingly, I submit that one of the core partnerships that needs to be fully developed in museums (and particularly art museums) is an honest and respectful relationship between the public and the institutions – a partnership in which the many meanings of art can be explored and honoured.
97. Traditional museums have been presenting views of :
(1) Artists
(2) Curators
(3) Viewers
(4) Governing authority
98. The creative process is completed by viewers in terms of :
(1) Style
(2) Form
(3) Content
(4) Subject matter
99. The visitor – centered half of the creative process is :
(1) Objective
(2) Subjective
(3) Prescriptive
(4) Descriptive
100. Which of the following statements is correct ?
(1) All viewers have their own individualistic interpretation.
(2) Viewers’ interpretation is same as the Curator.
(3) Viewers’ interpretation is same as the Artist.
(4) All viewers interpret in the same way.
Latest Govt Job & Exam Updates: